COSMIC Mutational Signatures: Release V3.2 (March 2021)
24 Mar 2021
We’d like to share our exciting new developments and updates for COSMIC Mutational Signatures in our v3.2 release.
COSMIC Mutational Signatures is a collaboration between Wellcome Sanger Institute, Cambridge, UK, COSMIC and the Alexandrov lab at the University of California, San Diego, USA, part of the wider Mutographs Cancer Grand Challenges Project.
In our latest release, you will be able to find the following:
New for Release v3.2
- We have added 6 new reference SBS mutational signatures in this release, taking our total to 107 reference signatures.
- SBS10c and SBS10d are two new signatures linked with polymerase proofreading deficiency (similar to SBS10a, SBS10b and SBS28), but in this case they are related to mutations in a different polymerase, POLD1.
- SBS91 was identified in normal cells from the cerebral cortex and the oesophageal squamous epithelium and its aetiology is unknown.
- SBS92 s a new mutational signature related to tobacco smoking.
- SBS92, SBS93 and SBS94 were extracted from the same dataset as version 3 signatures (PCAWG Consortium data) but are now using our newly developed computational method, SigProfilerExtractor.
- SBS10c and SBS10d are two new signatures linked with polymerase proofreading deficiency (similar to SBS10a, SBS10b and SBS28), but in this case they are related to mutations in a different polymerase, POLD1.
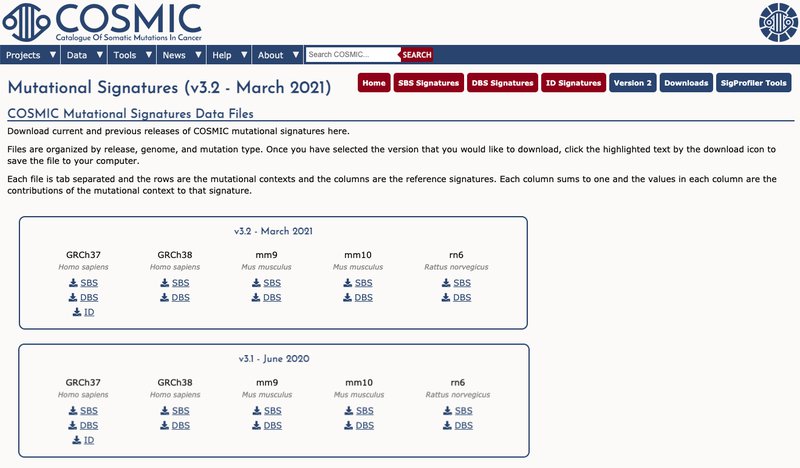
- We have created a new unified download page, serving as a one stop shop for the mutational signature profiles, grouped per release for all past releases from version 1 in 2013. This groups all reference signatures into a single file, organised by variant class (SBS, DBS and ID), genome (GRCh37, GRCh38, mm9, mm10, rn6) and the COSMIC Mutational Signatures release version. Our new downloads page can be found here.
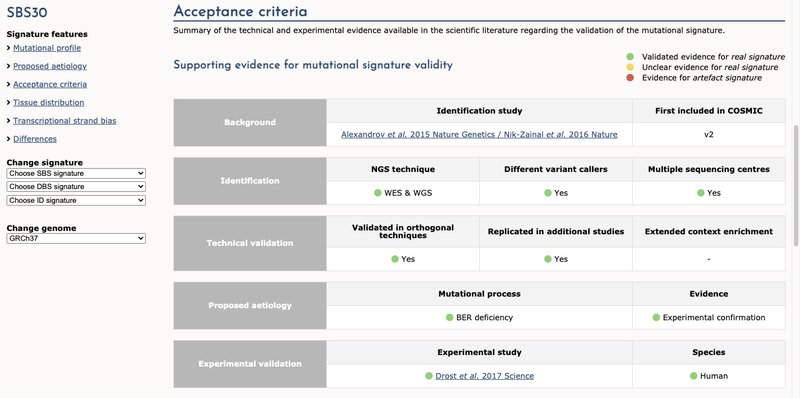
- We have added additional supporting evidence for the proposed aetiology of the signatures.
This high quality manually curated data can be used alongside the comments section to provide transparency and justification for why a signature is considered to be a reference signature or artefact.
In the example of signature SBS30, its aetiology was unknown when it was identified. However, it has later been experimentally proven that it was related to base excision repair deficiency due to NTHL1 mutation.
- It is now possible for all SBS and DBS signatures to be rendered with the newly added rn6 rat reference genome, alongside the pre-existing reference genomes GRCh37, GRCh38, mm9, and mm10 for all SBS and DBS signatures.
- We have increased the coverage and uniformity of our signatures and have corrected some errata in texts and images.
- To support the future development of COSMIC Mutational Signatures and better support our curators, we have conducted a technological overhaul to the website. As a part of this:
- The URL used to access Mutational Signatures has changed from https://cancer.sanger.ac.uk/cosmic/signatures becoming https://cancer.sanger.ac.uk/signatures. There will be no interruption to service as all of the links will be redirected to the new site.
- We have added better responsive layouts.
- We have also implemented a simplification and cleaner redesign of the website navigation.
If you have any comments or suggestions regarding what you would like to see in any of the COSMIC products, including COSMIC Mutational Signatures please email us on: cosmicengagement@sanger.ac.uk.
Please follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook and via our email announcements to keep abreast of the latest COSMIC news and developments. If you do not receive our emails, please update your email preferences, as shown below, in your COSMIC account.

